Ftp send command syntax
It can be used to transfer files to and from a remote network. Use only IPv4 to contact any host. Use passive mode for data transfers. Allows use of ftp in environments where a firewall prevents connections from the outside world back to the client machine. Requires that the ftp server support the PASV command. This is the default if invoked as pftp. Turns off interactive prompting during multiple file transfers. Restrains ftp from attempting "auto- login " upon initial connection.
If auto-login is enabled, ftp will check the. If no entry exists, ftp will prompt for the remote machine login name default is the user identity on the local machine , and, if necessary, prompt for a password and an account with which to login.
Disables command editing and history support, if it was compiled into the ftp executable. Verbose option forces ftp to show all responses from the remote server, as well as report on data transfer statistics.
The client host and an optional port number with which ftp is to communicate may be specified on the command line. If this is done, ftp will immediately attempt to establish a connection to an FTP server on that host; otherwise, ftp will enter its command interpreter and await instructions from the user. The following commands are recognized by ftp:. Invoke an interactive shell on the local machine.
If there are arguments , the first is taken to be a command to execute directly, with the rest of the arguments as its arguments. Execute the macro macro-name that was defined with the macdef command. Arguments are passed to the macro unglobbed. Supply a supplemental password required by a remote system for access to resources once a login has been successfully completed. If no argument is included, the user will be prompted for an account password in a non- echoing input mode.
Append a local file to a file on the remote machine. If remote-file is left unspecified, the local file name is used in naming the remote file after being altered by any ntrans or nmap setting.
File transfer uses the current settings for type, format, mode, and structure. Set the file transfer type to network ASCII. This is the default type. Terminate the FTP session with the remote server and exit ftp. An end of file will also terminate the session and exit.
Toggle remote computer file name case mapping during mget commands. When case is on default is off , remote computer file names with all letters in uppercase are written in the local directory with the letters mapped to lowercase.
Change the remote machine working directory to the parent of the current remote machine working directory. Change the permission modes of the file file-name on the remote system to mode. Terminate the FTP session with the remote server, and return to the command interpreter. Any defined macros are erased.
FTP Commands To Transfer FilesToggle carriage return stripping during ascii type file retrieval. When cr is on the default , carriage returns are stripped from this sequence to conform with the UNIX single linefeed record delimiter. Records on non-UNIX remote systems may contain single linefeeds; when an ascii type transfer is made, these linefeeds may be distinguished from a record delimiter only when cr is off. Toggle the printing of control characters in the output of ASCII type commands.
When this is turned on, control characters are replaced with a question mark if the output file is the standard output.
This is the default when the standard output is a tty. If an optional debug-value is specified it is used to set the debugging level. Print a listing of the directory contents in the directory, remote-directory, and, optionally, placing the output in local-file.
If interactive prompting is on, ftp will prompt the user to verify that the last argument is indeed the target local file for receiving dir output.
With command line FTP, how can I transfer a group of files without typing out all their names?
If no directory is specified, the current working directory on the remote machine is used. If no local file is specified, or local-file is - , output comes to the terminal. Retrieve the remote-file and store it on the local machine. If the local file name is not specified, it is given the same name it has on the remote machine, subject to alteration by the current case, ntrans , and nmap settings.
The current settings for type, form, mode, and structure are used while transferring the file. Toggle file name expansion for mdelete , mget and mput. If globbing is turned off with glob , the file name arguments are taken literally and not expanded. Globbing for mput is done as in csh. For mdelete and mget , each remote file name is expanded separately on the remote machine and the lists are not merged. Expansion of a directory name is likely to be different from expansion of the name of an ordinary file: That can be done by transferring a tar archive of the subtree in binary mode.
Toggle hash-sign " " printing for each data block transferred. The size of a data block is bytes. Print an informative message about the meaning of command. If no argument is given, ftp prints a list of the known commands. Set the inactivity timer on the remote server to seconds seconds.
If seconds is omitted, the current inactivity timer is printed. Change the working directory on the local machine. If no directory is specified, the user's home directory is used.
Print a listing of the contents of a directory on the remote machine. If remote-directory is left unspecified, the current working directory is used. If interactive prompting is on, ftp will prompt the user to verify that the last argument is indeed the target local file for receiving ls output.
Subsequent lines are stored as the macro macro-name; a null line consecutive newline characters in a file or carriage returns from the terminal terminates macro input mode. There is a limit of 16 macros and total characters in all defined macros. Macros remain defined until a close command is executed. Like dir , except multiple remote files may be specified. If interactive prompting is on, ftp will prompt the user to verify that the last argument is indeed the target local file for receiving mdir output.
Expand the remote-files on the remote machine and do a get for each file name thus produced. See glob for details on the file name expansion. Resulting file names will then be processed according to case, ntrans , and nmap settings.
Like nlist , except multiple remote files may be specified, and the local-file must be specified. If interactive prompting is on, ftp will prompt the user to verify that the last argument is indeed the target local file for receiving mls output.
Set the file transfer mode to mode-name. The default mode is " stream " mode.
Expand wild cards in the list of local files given as arguments and do a put for each file in the resulting list. See glob for details of file name expansion.
Resulting file names will then be processed according to ntrans and nmap settings. Get the file only if the modification time of the remote file is more recent that the file on the current system. If the file does not exist on the current system, the remote file is considered newer.
Otherwise, this command is identical to get. Print a list of the files in a directory on the remote machine. If interactive prompting is on, ftp will prompt the user to verify that the last argument is indeed the target local file for receiving nlist output. If no local file is specified, or if local-file is - , the output is sent to the terminal. Set or unset the file name mapping mechanism. If no arguments are specified, the file name mapping mechanism is unset. If arguments are specified, remote file names are mapped during mput commands and put commands issued without a specified remote target file name.
If arguments are specified, local file names are mapped during mget commands and get commands issued without a specified local target file name. This command is useful when connecting to a non-UNIX remote computer with different file naming conventions or practices. The mapping follows the pattern set by inpattern and outpattern. All other characters are treated literally, and are used to determine the nmap [ inpattern ] variable values.
The outpattern determines the resulting mapped file name. Spaces may be included in outpattern , as in the example: Set or unset the file name character translation mechanism. If no arguments are specified, the file name character translation mechanism is unset.
If arguments are specified, characters in remote file names are translated during mput commands and put commands issued without a specified remote target file name. If arguments are specified, characters in local file names are translated during mget commands and get commands issued without a specified local target file name.
FTP commands
Characters in a file name matching a character in inchars are replaced with the corresponding character in outchars. If the character's position in inchars is longer than the length of outchars , the character is deleted from the file name. Establish a connection to the specified host FTP server. An optional port number may be supplied, in which case, ftp will attempt to contact an FTP server at that port.
If the auto-login option is on default , ftp will also attempt to automatically log the user in to the FTP server see below. Interactive prompting occurs during multiple file transfers to allow the user to selectively retrieve or store files. If prompting is turned off default is on , any mget or mput will transfer all files, and any mdelete will delete all files.
Execute an ftp command on a secondary control connection. This command allows simultaneous connection to two remote ftp servers for transferring files between the two servers. The first proxy command should be an open, to establish the secondary control connection. Enter the command "proxy? The following commands behave differently when prefaced by proxy: Third party file transfers depend upon support of the ftp protocol PASV command by the server on the secondary control connection.
Store a local file on the remote machine. If remote-file is left unspecified, the local file name is used after processing according to any ntrans or nmap settings in naming the remote file.
If local-file does not exist ftp won't fetch the file. This command is useful when transferring very large files over networks that are prone to dropping connections. Request help from the remote FTP server. If a command-name is specified it is supplied to the server as well. With no arguments, show status of remote machine. If file-name is specified, show status of file-name on remote machine. Resynchronization may be necessary following a violation of the ftp protocol by the remote server.
Restart the immediately following get or put at the indicated marker. On UNIX systems, marker is usually a byte offset into the file.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP), a List of FTP Commands
Toggle storing of files on the local system with unique file names. If a file already exists with a name equal to the target local file name for a get or mget command, a ".
If the resulting name matches another existing file, a ". If this process continues up to ". The generated unique file name will be reported. Note that runique will not affect local files generated from a shell command see below. The default value is off. Toggle the use of PORT commands. By default, ftp will attempt to use a PORT command when establishing a connection for each data transfer.
The use of PORT commands can prevent delays when performing multiple file transfers. If the PORT command fails, ftp will use the default data port. When the use of PORT commands is disabled, no attempt will be made to use PORT commands for each data transfer. This is useful for certain FTP implementations which do ignore PORT commands but, incorrectly, indicate they've been accepted.
Set the file transfer structure to struct-name. By default "stream" structure is used.
Toggle storing of files on remote machine under unique file names. The remote ftp server must support the ftp protocol STOU command for successful completion. The remote server will report unique name.
Default value is off. Set the file transfer type to type-name. If no type is specified, the current type is printed. The default type is network ASCII. Set the default umask on the remote server to newmask. If newmask is omitted, the current umask is printed.
Identify yourself to the remote FTP server. If the password is not specified and the server requires it, ftp will prompt the user for it after disabling local echo.
If an account field is not specified, and the FTP server requires it, the user will be prompted for it. If an account field is specified, an account command will be relayed to the remote server after the login sequence is completed if the remote server did not require it for logging in. Unless ftp is invoked with " auto-login " disabled, this process is done automatically on initial connection to the FTP server. In verbose mode, all responses from the FTP server are displayed to the user.
How do I use FTP from a command line?
In addition, if verbose is on , when a file transfer completes, statistics regarding the efficiency of the transfer are reported. By default, verbose is on. Command arguments which have embedded spaces may be quoted with quote " marks.
To abort a file transfer, use the terminal interrupt key usually Ctrl-C. Sending transfers will be immediately halted. Receiving transfers will be halted by sending a ftp protocol ABOR command to the remote server, and discarding any further data received. The speed at which this is accomplished depends upon the remote server's support for ABOR processing. The terminal interrupt key sequence will be ignored when ftp has completed any local processing and is awaiting a reply from the remote server.

A long delay in this mode may result from the ABOR processing described above, or from unexpected behavior by the remote server, including violations of the ftp protocol. If the delay results from unexpected remote server behavior, the local ftp program must be killed manually. Files specified as arguments to ftp commands are processed according to the following rules:.
If the shell command includes spaces, the argument must be quoted; e. A particularly useful example of this mechanism is: Failing the above checks, if " globbing " is enabled, local file names are expanded according to the rules used in the csh ; c.
If the ftp command expects a single local file. For mget commands and get commands with unspecified local file names, the local file name is the remote file name, which may be altered by a case , ntrans , or nmap setting. The resulting file name may then be altered if runique is on.
For mput commands and put commands with unspecified remote file names, the remote file name is the local file name, which may be altered by a ntrans or nmap setting. The resulting file name may then be altered by the remote server if sunique is on. The FTP specification specifies many parameters which may affect a file transfer. The type may be one of " ascii ", " image " binary , " ebcdic ", and "local byte size" for PDP 's and PDP's mostly.
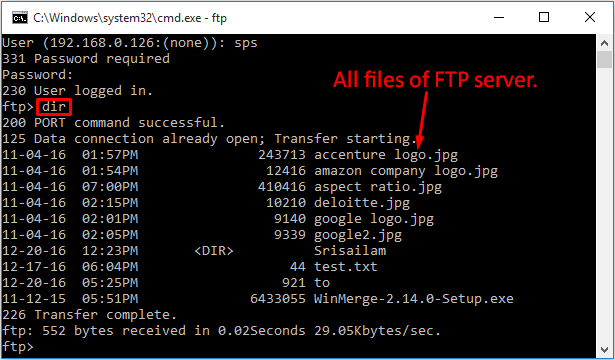
The ftp command makes use of the following environment variables:. The above command instructs ftp to attempt a connection to exampleftp. Below is an example of what would be seen:. If your user name and password are valid and entered correctly, you will be successfully logged in:. The first thing you'd probably want to do is see what directory that is. To see the present working directory, use the pwd command just like in Linux:. The number is a numerical code. All FTP messages have a code number associated with them, and for technical reasons they are included with the messages from the server.
Let's see what files are in there, using the ls command:. This will produce a file listing, just like in Linux. You can change remote directories with cd. If you want to change what directory you're using on your local computer, you can use lcd for "local change directory.
That's not quite right. JPEG images are binary files, not ASCII text files. FTP supports two different types of file transfers, ASCII and binary. At login, the server told us it was currently in ASCII mode. Let's change that to binary:. We can now do the same file transfer and the file will come through correctly. This directory had a "README" message which is displayed by the FTP server every time you change it to your current directory. The server then let you know that your cd command was successful.
Now let's download every JPEG file using a wildcard. We can use the mget command, which allows us to get multiple files with one command:. We will now get all the jpeg files with the extensions JPG , JPEG , jpg , or jpeg. If we have any files to upload to the server, we can use the commands put or mput to upload them. When we're done, we can logout using the exit command.
Search Help Tips Dictionary History Forums Contact. Home Help Linux and Unix. Linux ftp command Updated: About ftp ftp syntax ftp examples Related commands Linux and Unix commands help. Was this page useful? Yes No Feedback E-mail Share Print.
Set the file transfer type to support binary image transfer. Allow the address resolver to return any address family.